Plant foods are given priority in whole-foods and plant-based diets, whereas processed meals and animal products are reduced. The whole foods plant based diet is linked to a number of health advantages, including a decreased risk of diabetes and a decrease in body weight.
Diets that prioritize whole, fresh foods and limit processed foods are better for overall health, according to the health and wellness communities. That’s what the plant-based, whole-foods diet does.
It emphasizes vegetables and less processed diets. Research indicates that plant-based diets can effectively promote weight loss and enhance overall health.
This article goes over all you need to know about a whole foods plant based diet, including foods to consume, potential health advantages, and an example meal plan.
What is a whole foods plant based diet?
The term “whole-foods, plant-based diet” (WFPB diet) has no precise definition. This approach is more of a lifestyle than a strict diet.
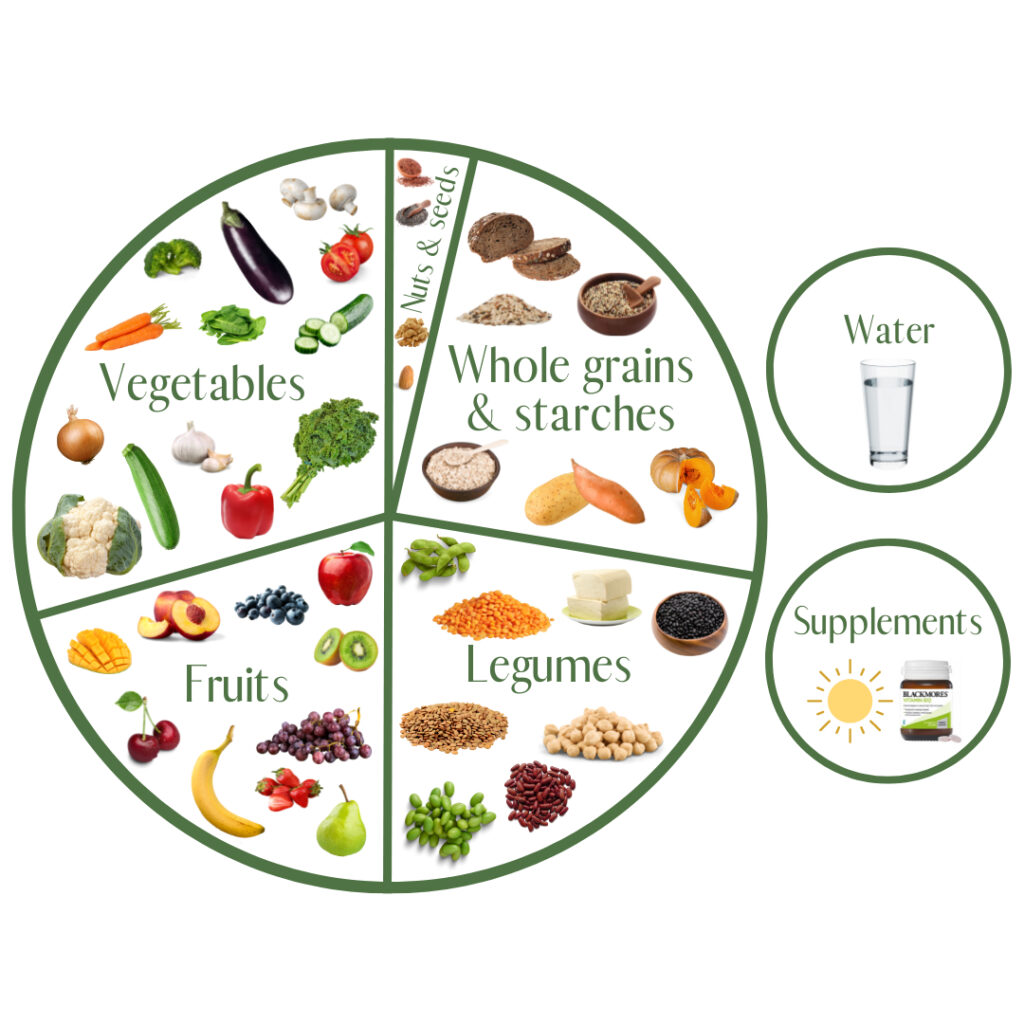
This is due to the fact that plant-based diets can differ significantly based on how much an individual consumes animal products.
However, the following are the fundamentals of a plant-based, whole-foods diet:
- Limits or stays away from animal products and prioritizes whole, minimally processed foods.
- Emphasizes plant-based foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, seeds, and nuts, while limiting refined foods, such as processed oils, white flour, and added sugars, in the bulk of your diet.
- Pay close attention to food quality; many WFPB diet advocates advocate for organic, locally produced food whenever feasible.
- Because of these factors, this diet is frequently mistaken for vegetarian or vegan diets. These diets are not the same, despite certain similarities.
Items to include in a plant-based, whole-foods diet
Animal items dominate most meals for many individuals, from morning (eggs and bacon) to dinner (steak).
Make plant-based foods the focal point of your meals as you make the switch to a plant-based diet. If you do consume animal products, do so sparingly and with consideration for their quality.
Milk products, eggs, poultry, meat, and fish are not the main focus of a plant-based diet; rather, they are utilized only as a supplement.
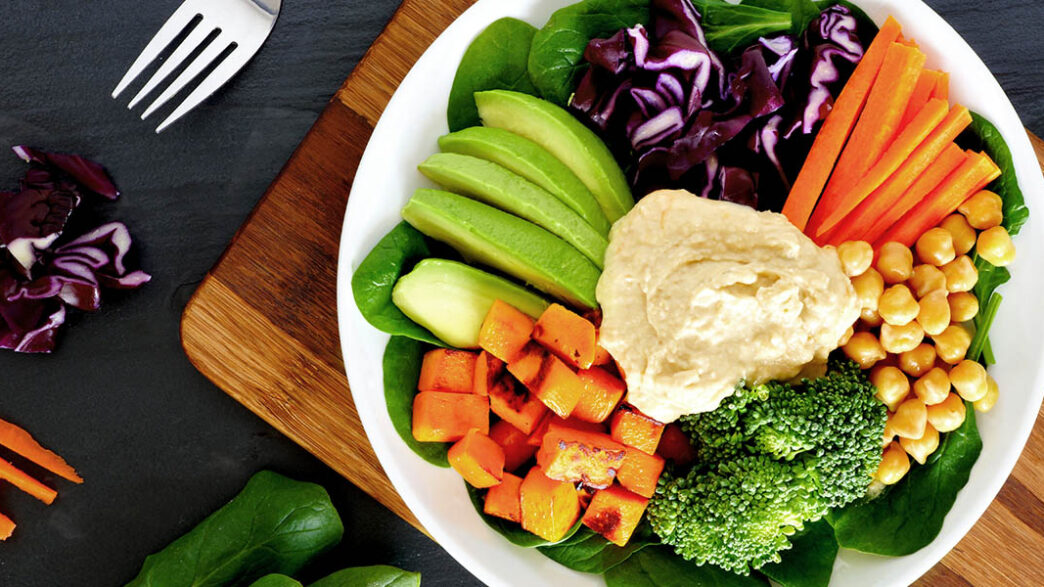
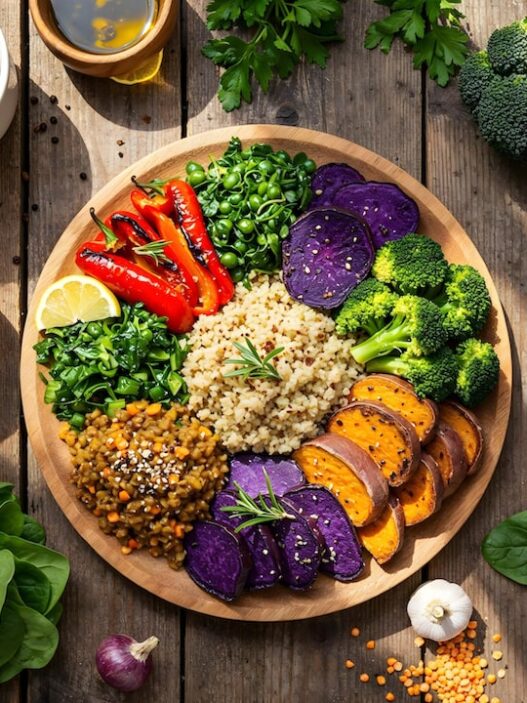
A whole foods plant based diet Food list
- Fruits include bananas, pineapple, pears, peaches, berries, and citrus fruits.
- Kale, spinach, peppers, tomatoes, broccoli, cauliflower, carrots, asparagus, and so forth are examples of vegetables.
- Starchy veggies include butternut squash, sweet potatoes, and potatoes.
- Whole grains include barley, quinoa, farro, rolled oats, brown rice, and brown rice pasta.
- Good fats include avocados, olive oil, unsweetened coconut, and so forth.
- Peas, chickpeas, lentils, peanuts, black beans, and so forth are examples of legumes.
- Almonds, cashews, macadamia nuts, sunflower seeds, pumpkin seeds, natural peanut butter, tahini, and other nuts, seeds, and nut butters.
- Plant-based milks without added sugar, such as cashew, almond, and coconut milk.
- Curry, black pepper, salt, turmeric, basil, rosemary, and other spices and herbs are examples of seasonings.
- Ingredients: soy sauce, vinegar, lemon juice, mustard, salsa, nutritional yeast, etc.
- Plant-based protein: tofu, tempeh, or powdered plant-based protein sources free of artificial additives or added sugar
- Drinks: tea, coffee, sparkling water, etc.
If you’re adding animal products to your plant-based diet, pick high-quality items from supermarkets or, even better, buy them from nearby farms.
Moderate consumption of animal products can include the following examples:
- Eggs.
- Pork, beef, and poultry
- dairy and seafood products
Some consumers might select pasture-raised food due to personal preferences or environmental concerns.
Items to limit or stay away from on WFPB diet
Excluding highly processed foods, the WFPB diet emphasizes eating foods in their most natural state.
When buying groceries, pay attention to what’s fresh and look for products with the fewest ingredients on labels.
- Fast food includes things like cheeseburgers, chicken nuggets, hot dogs, and French fries.
- Table sugar, soda, juice, pastries, cookies, candies, sweet tea, and sugary cereals are examples of added sugars and sweets.
- Processed grains, like bagels, white bread, white rice and white pasta.
- Convenience and packaged foods include cereal bars, chips, crackers, frozen entrees, and more.
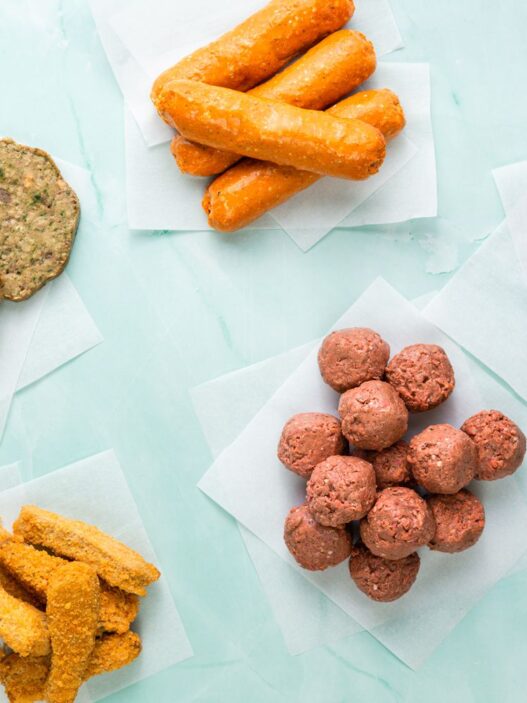
- Processed vegan-friendly goods, such as vegan butters, imitation cheeses, and plant-based meats like Tofurkey.
- Sweet’N Low, Splenda, Equal, and other artificial sweeteners.
- Processed animal goods, such as beef jerky, sausage, bacon, and lunch meats.
If you want a sample meal plan, you can find it here.
What Does The Research Say About WFPB Diet?
Those who ate a nutritious plant-based diet high in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, and nuts had a far lower risk of heart disease than those who did not, according to a big, older study conducted in 2017 with over 200,000 participants.
A plant-based diet may lower your chance of developing some types of cancer, according to research. A healthy plant-based diet may be linked to a lower risk of breast cancer, according to a study including over 169,000 participants.
Likewise, a recent study found that eating more nutrient-dense plant-based foods was linked to a decreased risk of aggressive prostate cancer, particularly in males under 65.
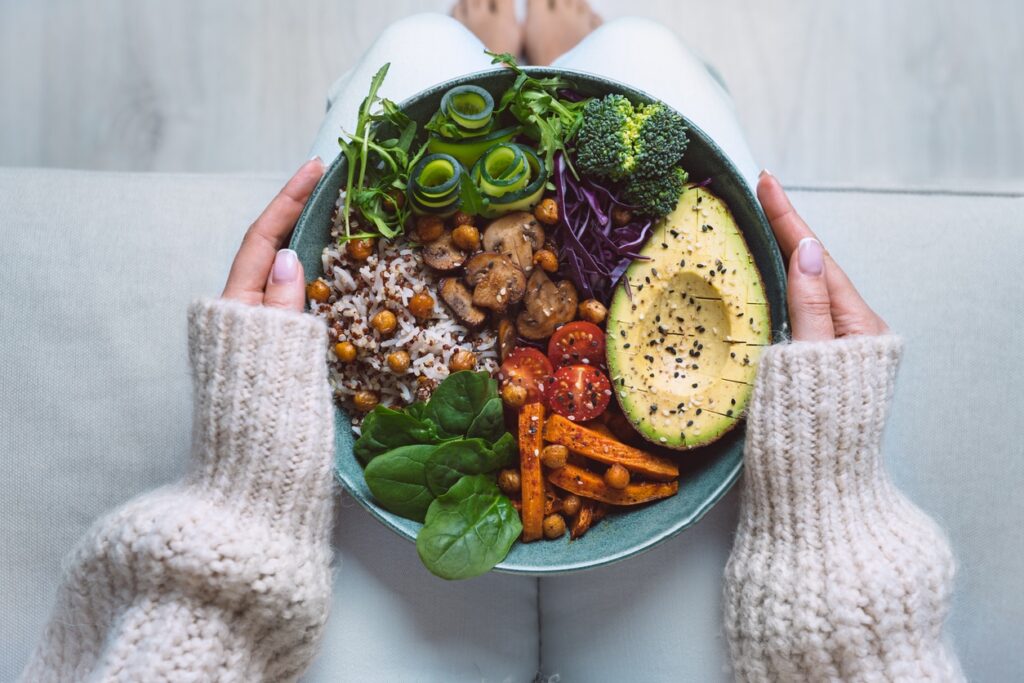

According to certain research, diets high in fruits and vegetables may assist older persons avoid or slow down cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease.
Higher levels of plant chemicals and antioxidants found in plant-based diets may help cure cognitive deficiencies and reduce the progression of Alzheimer’s disease, according to several animal and test-tube studies.
In Conclusion
Switching to a whole foods plant based diet is one of the most effective ways to enhance your health, increase your energy levels, and fend off chronic illnesses. Research indicates that altering your diet can help you maintain a healthy weight, extend your life, and protect the environment.
There is strong scientific evidence that a plant-based, whole-food diet can prevent, control, or even reverse a number of chronic conditions.