Hello Fitness Explorers !!!
A weight-loss journey isn’t about eating less, it’s all about eating in the right way.
A weight loss nutrition diet is highly focused on balanced meals that fuel your body, support your metabolism, and help in burning fat while preserving muscle.
By taking some steps, for example choosing nutrient-dense foods, controlling portions, and maintaining consistency, you can easily achieve sustainable results without feeling deprived.
Optimal Diet Strategies For Weight Loss and Weight Loss Maintenance
Obesity has become one of the most important public health problems all over the world , which suggests the need for evidence-based dietary strategies for weight loss and the maintenance of your weight. Weight management depends upon some complex factors such as amount of food eaten, type of food eaten, and the timings of meals.
We identified evidence-based dietary strategies for weight management which are based on these three components.
An energy deficit is the most important factor during your weight loss. A low-calorie diet with a low fat or carbohydrate content has been highly recommended; however, in some cases, a very-low-calorie diet is required for a short period of time.
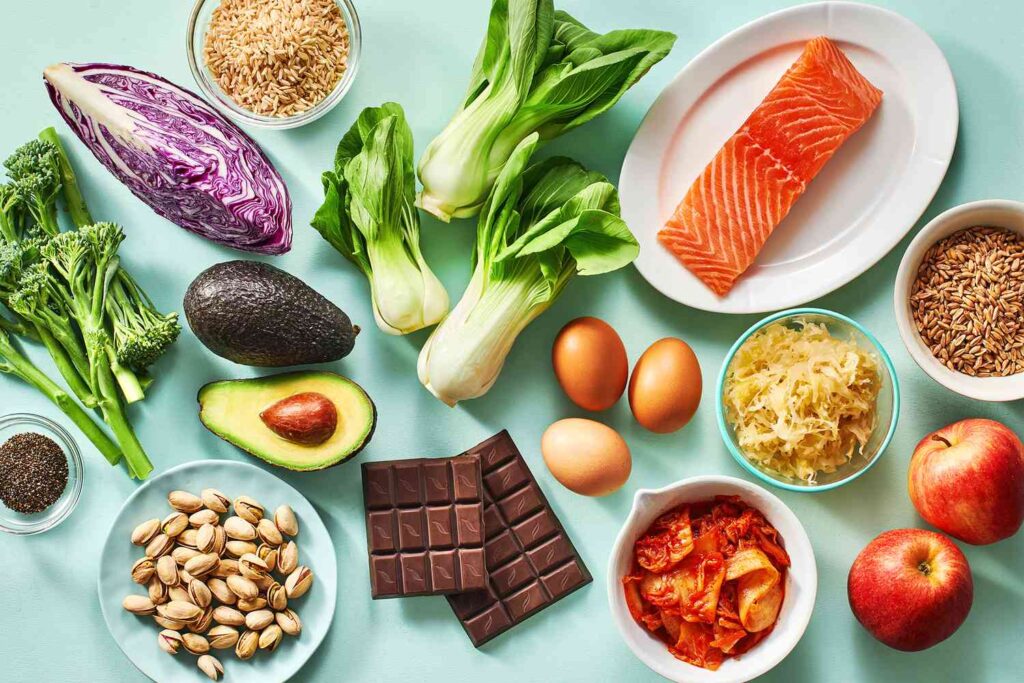

Some macronutrient composition-based diets, for example ketogenic diet or high-protein diet, could be considered in some cases, although the potential risks and long-term effectiveness remain unknown.
Meal timing is also an important factor in weight management, and breakfasts that are higher in calories ,in combination with overnight fasting may help to prevent obesity.
Our review indicated that there is no single best strategy for weight management. Hence, the strategies for weight loss and its maintenance should be individualized (dependent on individual health) and healthcare providers must choose the best strategy based on patient preferences.
Research About Weight-loss Nutrition Diet
More than 650 million individuals over the world suffer from obesity, and the prevalence of this condition has increased rapidly during the past 50 years.
Obesity has become one of the most prominent public health problems globally and is strongly associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular(heart) diseases which includes myocardial infarction (heart attack) and stroke, osteoarthritis, obstructive sleep apnea, depression, and some types of cancer, such as breast, ovarian, prostate, liver, kidney, intestinal and colon cancer.
Optimal Diets
Optimal diets for weight management have been a topic of debate not only among researchers, nutrition experts, and healthcare professionals, but also among the public.
According to analysis of several diet programs, calorie deficit was the primary driver of weight loss, which is followed by macronutrient composition.
Another study explored the effects of popular diets without specific calorie targets and showed that the Atkins diet resulted in clinically meaningful weight loss only after 6 months.
Contrary to it, another review revealed that the Atkins, Weight Watchers, and Zone diets resulted in modest and similar long-term weight loss after a year.
Recently, intermittent fasting and time-restricted eating have become popular and seem to be effective for weight loss for many people.
However, several questions remain unanswered. Does a high-protein diet helps in weight loss and its maintenance? Can a ketogenic diet burn fat effectively? Do carbohydrates increase fat?
Can intermittent fasting help in losing weight? New information about diet has only added to the current confusion due to several controversial dietary regimens, and there is no proper guidance on the optimal diet for weight loss.
Factors That Affect Obesity
Obesogenic environments and biological and psychological factors all contribute to obesity.
However, obesogenic environments, which includes social determinants, cultures, and food supply systems, proved to be challenging to modify. Therefore, dietary interventions are the cornerstone of weight-management strategies, and pharmacologic and surgical interventions also aim to improve dietary management.
Complex factors shape and influence diets, especially for weight management. However, the amount of food eaten, type of food consumed (macronutrient composition), and the timings of meals are the key components of weight-management strategies.
In this review, we discuss evidence-based dietary interventions for weight loss and weight-loss management based on these components.
AMOUNT OF FOOD INTAKE
Low-Calorie Diet VS Very-Low-Calorie Diet
The main component of diets for weight loss and weight-loss maintenance is basically an energy deficit. Under the “calories-in, calories-out” model, dietary management has focused on the concept of “eat less, move more,” and patients have been advised to calculate their calorie balance whenever they eat.
But actually ,energy intake and energy expenditure are dynamic processes influenced by body weight and influence each other too. Therefore, interventions aimed at creating an energy deficit through the diet are countered by physiological adaptations that resist weight loss.
A low-calorie diet involves consumption of 1,000–1,500 calories per day,deficits of 500–750 calories per day have been used for weight loss and are recommended by many obesity societies and guidelines.
Low-calorie diets restrict fats or carbohydrates, neither of which has been determined to be more important for weight loss if only a calorie deficit occurs. The 2018 the Diet Intervention Examining The Factors Interacting with Treatment Success (DIETFITS) study found no any significant differences in weight loss between low-fat and low-carbohydrate diets.
However, meal planning and meal preparation take effort, and weight-loss maintenance requires a sustained low-calorie diet . Moreover, metabolic adaptations to decrease energy expenditure can lead to a plateau with this type of diet, which individuals may misinterpret as “failure” due to “lack of consistency.”
Traditionally, a very-low-calorie diet (VLCD), which provides <800 kcal a day, is not recommended for routine weight management and should only be used in limited circumstances along with medical monitoring according to obesity guidelines and this diet is not considered as a healthy diet or healthy way to lose weight.
Meal Replacements
The meal replacements include not only products that are marketed as soups, shakes, and bars, but also portion-controlled, ready-made meals.
These replacements are used instead of “normal” food for one or more meals to reduce the daily calorie intake.
Meal replacements can be useful for calorie-control because people tend to overestimate or underestimate the amount of calories in food.
A systematic review showed the importance of meal replacement in weight loss, that demonstrate a mean difference of –2.22 to –6.13 kg compared with other diets involving support alone.
Despite their availability and affordability, meal replacements are typically not successful for maintaining weight loss over a long duration.
Weight-Loss and Maintenance Strategies
The most essential component of an effective weight-management program should be the prevention of unwanted weight gain from excess body fat.
The military is in unique position to give attention on the prevention from the first day of an individual’s military career, the reason is that military population is selected from a pool of individuals who meet specific criteria for body mass index (BMI) and percent body fat, the primary goal should be to foster an environment that promotes the maintenance of a healthy body weight and body composition throughout an individual’s military career.
There is significant evidence that losing body fat which is in excessive amount is difficult for most individuals and the risk of regaining lost weight is also high.
From the first day of initial entry training, an understanding of the fundamental causes of excess weight gain must be communicated to each individual, along with a plan that helps in maintaining a healthy body weight as a way of life.
Here are some ways to make your body healthy.
These are mentioned below:
- Physical Activity
- Behavior and lifestyle modification
- Self-Monitoring And Feedback
- Nutrition Education
What’s The Best Diet For Weight Loss ?
It’s a query in the minds of most people once they’ve decided they need loose some pounds, what is the best diet for their weight loss?
While that’s not an unreasonable question, it suggests an approach that is less than optimal, which is to plan on adopting a radically restrictive mode of eating for a while until the weight is lost, and then going back to eating as normal.
Instead of embracing quick diets, people who have lost weight and kept it off usually have made a permanent shift towards healthier eating habits.
Simply replacing unhealthy foods with healthy ones not only for a few weeks, but forever will help you in achieving weight loss while offering many other benefits. So a better set of questions might be, “What is a healthy diet? What does a healthy diet look like?”
A healthy diet focuses on natural and unprocessed foods over prepackaged meals and snacks. It is balanced, and provides your body with all the nutrients and minerals it needs to function properly.
This diet emphasizes plant based foods, especially fruits and vegetables, over animal foods. It contains a plenty of protein. The diet is low in sugar and salt. It incorporates healthy fats including fish, olive oil, and other plant-derived oils.
Healthy Eating Plan
Do you know what healthy eating gives to your body?
A healthy eating plan gives your body the nutrients your body needs in your daily life meals while staying within your daily calorie goal for weight loss. It also lowers your risk for cardiovascular diseases and other health conditions.
A Healthy Eating Plan
This emphasizes vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and fat-free or low-fat dairy products,which has following characteristics
- Includes lean meats, poultry, fish, beans, eggs, and nuts
- Limits saturated and trans fats, sodium, and added sugars
- Controls portion sizes
- Calories count
To lose weight, most people need to reduce the number of calories they get from food and beverages and increase their physical activity. In simple words, they bring the energy into their body and release it out.
For a weight loss of 1–1 ½ pounds per week, daily intake should be reduced by 500 to 750 calories.
In general, eating plans that contain1,200 to 1,500 calories per day will help most women in loosing weight safely.
Eating plans that contain 1,500–1,800 calories each day are suitable for men and for women who weigh more or who exercise regularly.
Very low calorie diets of fewer than 800 calories per day should not be used unless you are being monitored by your doctor,it is an unhealthy way to reduce weight.
Diet Plans
I’m giving you the basic idea of the meals that you can use in your diet to live a healthy life.
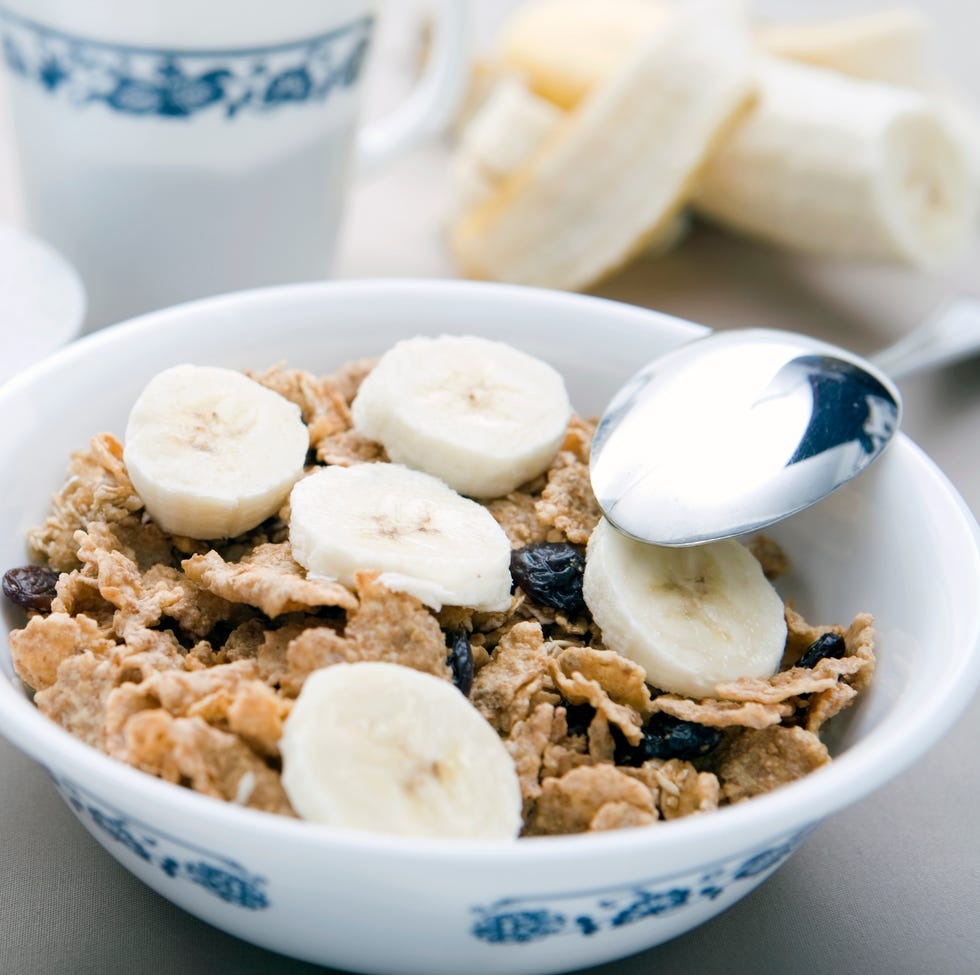
1. Breakfast
Pour 3/4 cup bran flakes, 1 banana and 1 cup fat-free milk in a bowl and combine them.

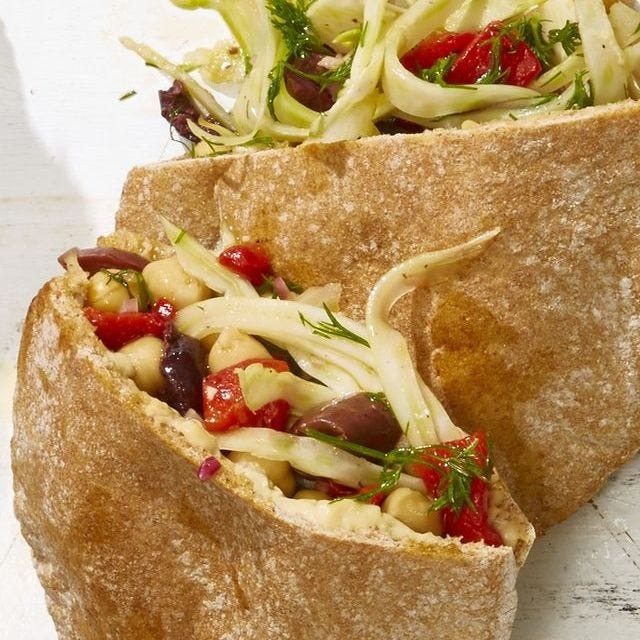
Lunch
Make a sandwich with 1 mini whole wheat bread, 3 ounces chicken breast, 1/2 roasted pepper, 1 teaspoon mayo, mustard and lettuce. Serve with 1 stick part-skim mozzarella string cheese and a serving of fruit, like 2 kiwis.

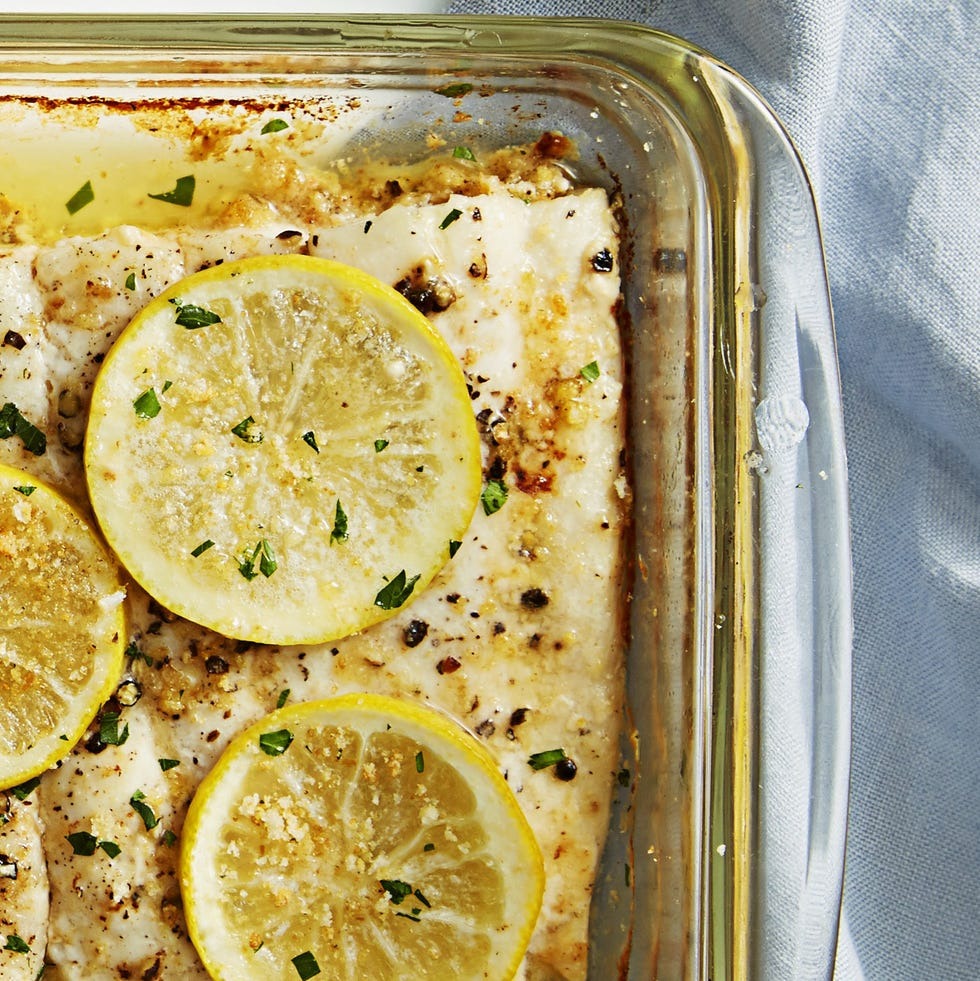
Dinner
Serve 4 ounces of flounder ( Zesty Lemon-Herb recipe is under 200 calories). Eat with 1 cup cooked couscous and 1 cup steamed broccoli. Enjoy with a single-serve ice cream for dessert.

Conclusion
A weight-loss nutrition diet is highly focused on healthy and balanced eating manners rather than strict restrictions on your diet. Choosing whole foods like fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains helps the body in staying energetic while reducing excess calories from the body.
Portion control and mindful eating are the key to prevent one from overeating. Staying hydrated and combining diet with regular exercise helps in supporting weight management. Overall, a sustainable and manageable diet builds long-term habits for better health and lasting results.