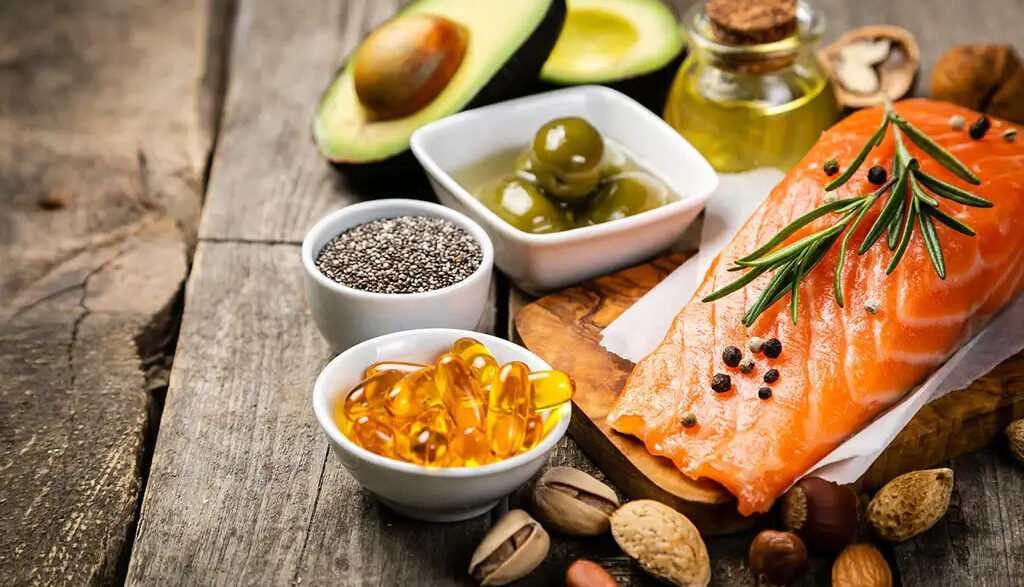
Medium chain triglycerides (MCTs) are fat molecules that are made up from oils like coconut and palm kernel oils. Some dietary fats are known as long-chain triglycerides.
MCTs or MCT foods are recognized as a source of fats for people who can’t tolerate the other types of fats. These fats might also help to reduce weight because the body is more vulnerable to break them down into molecules that are called ketone bodies. These ketone bodies can be used as a source of energy too.
MCT Supplements
Introduction To MCT Supplements
Medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs) have gained attention over the last two decades because they have unique chemical structure, metabolic advantages, and potential health benefits too.
Long-chain triglycerides (LCTs), require complex digestion but MCTs are absorbed immediately and metabolized into ketones that are used as an alternative energy substrate for your brain and muscles.
MCT supplements are the concentrated forms of the fatty acids mentioned above, most of them are made from coconut oil or palm kernel oil.
We can get them in the form of oils, powders, or capsules and are marketed for weight management, athletic performance, cognitive health, and clinical nutrition support.
Composition
These fibers are rich in acids like caprylic acid (C8) and capric acid (C10), because these two acids provide the fastest conversion of fats into ketones.
Popularity
These ketones are common among low-carb or ketogenic diets, but are also prescribed clinically for people who are suffering from malabsorption disorders
Chemistry And Structure
Triglycerides consist of three fatty acids that are tightly bound to a glycerol backbone. The chain length of these fatty acids determines how they are actually absorbed and metabolized
Short-Chain Fatty Acids (SCFA)
This chain contains 2-6 carbons. These are produced in the colon by fermentation of dietary fiber.
Medium-Chain Fatty Acids (MCFA)
This chain contains 6-8 carbons. These carbons are C6 caproic, C8 caprylic, C10 capric, C12 lauric.
Long-Chain Fatty Acids (LCFA)
This chain contains 13–21 carbons.
Very Long-Chain Fatty Acids (VLCFA)
This is the longest chain which consists of more than 22 carbons.
MCTs are those glycerol molecules which contain MCFA side chains. If they are shorter in length ,then they give a lower molecular weight, higher solubility, and faster metabolism compared to LCTs
Health Benefits of MCT Supplements
The main benefit of MCT supplement is a following
Weight Management And Metabolism
MCTs may help in enhancing satiety and also lead to reducing the daily intake of calories as compared to LCTs.
They are slightly less energy-dense than LCTs9. As, MCTs contain 8.3kcal/g and LCTs contain 8.3kcal/g.
Some clinical trials predict some reductions in the body and fat mass with regular use.
Example Study
A randomized controlled trial that was published in The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found that participants that are overweight and consume MCT oil reduced more fat as compared to those who are consuming olive oil over almost 16 weeks.
Ketogenic Energy and Brain Health
Since MCTs are converted into ketones, they are used in ketogenic diets to
- Increase mental clarity and cognitive performance.
- Support patients who suffer from epilepsy (especially children who are resistant to medications).
- Improve mild MCI and Alzheimer’s disease outcomes.
Ketones are known as an alternative energy substrate for neurons, which are particularly important in neurodegenerative conditions where glucose metabolism is impaired.
MCT Oil Whole Foods
MCT oil is basically a concentrated source of healthy fats that are naturally found in whole foods such as coconut oil, palm kernel oil, and dairy products like butter and cheese.
MCTs are quickly absorbed and converted into energy by the liver, making them a popular choice for boosting mental focus, supporting weight management, and enhancing athletic performance.
While MCT oil itself is a refined product, its whole food sources like coconuts and grass-fed dairy also provide additional nutrients, including fiber, vitamins, and minerals that contribute to overall health. Incorporating these whole food sources into your diet can offer the benefits of MCTs in a more natural and nutrient-rich form.
Forms Of MCT Supplements
MCT Oil
This is a pure or blended form of liquid,which is commonly added to coffee, smoothies, or salads.
MCT Powder
This is actually the oil bound to a carrier (fiber or protein), proved to be easy to digest and more convenient for travel.
MCT Capsules/Softgels
Portable but usually lower dosages.
Medical MCT Formulas
Used clinically (e.g., MCT-based enteral feeds).
Clinical And Medical Uses
Epilepsy is the part of the MCT ketogenic diet, which allows a higher carb or protein intake while still producing ketosis.
Alzheimer’s Disease
Long-term MCT supplementation may stabilize or improve cognition in some patients.
Fat Malabsorption Disorders
Provides easily absorbed calories in patients with pancreatic or biliary dysfunction.
Limitations And Controversies
Weight Loss
The benefits of MCTs are often modest and not a substitute for diet or exercise.
Cardiovascular Health
MCTs may slightly cause a rise in triglycerides, creating an impact on cholesterol that remains debated.
Environmental Concerns
Palm kernel oil too raises sustainability issues.
Research Gaps
More long-term research is needed for some health conditions like dementia and metabolic syndrome.
Summary
MCT supplements give these benefits,as they are rapidly absorbed, easily digested fats that can enhance your energy level, support ketosis, help in treating digestive disorders, and also improve brain health.
Key Takeaway
MCT supplements are most beneficial when used strategically for patients with fat malabsorption, individuals on ketogenic diets, and possibly for cognitive support. However, they should be introduced gradually, with attention to dosage and product quality.
MCT Oil Supplement
What Is MCT Oil?
MCT oil is commonly found in concentrated form of medium-chain triglyceride supplementation. MCT oil is made to give pure MCTs which are usually caprylic acid (C8), capric acid (C10), or blends of the two.
C8 (Caprylic acid)
It is considered the “premium” form, because it converts most efficiently into ketones and is less likely to cause digestive problems.
C10 (Capric acid)
Slightly slower to metabolize than C8, but still faster than C12 (lauric acid).
C12 (Lauric acid)
Often excluded in purified MCT oils, since it behaves more like a long-chain fatty acid in metabolism.
Most commercial MCT oils are fractionated from coconut oil (which is ~55–65% MCTs) or palm kernel oil.
Fractionation is a refining process that causes separation of MCTs from longer fatty acids.
Metabolic Pathway Of MCT Oil
The metabolism of MCT oil is the reason behind its growing popularity
Rapid Absorption
Unlike long-chain fats, MCTs in oil form bypass the lymphatic system.
Immediate Transport
They travel via the portal vein to the liver.
Quick Conversion
In the liver, MCTs undergo β-oxidation and rapidly form ketone bodies.
Ketone Utilization
These ketones are then circulated in the blood as a quick energy source for muscles and brain cells.
This is why MCT oil is particularly valued in ketogenic diets and for neurological health.
Benefits Of MCT Oil Supplementation
Weight Management
MCT oil is often marketed for weight loss. While not a “magic bullet,” research shows modest benefits:
Satiety
MCTs promote feelings of fullness by stimulating the release of peptide YY and leptin, two hormones that regulate appetite.
Increased Fat Oxidation
MCTs may help the body burn more fat compared to LCTs.
Lower Energy Density
At 8.3 kcal/g, they provide slightly fewer calories than standard fats (9 kcal/g).
Clinical Evidence
A 12-week randomized controlled trial found that overweight adults who consumed MCT oil as part of their diet lost more weight and had greater fat reduction than those consuming olive oil.
Ketogenic Diet Support
MCT oil is especially important for people following a ketogenic diet. It raises blood ketone levels more quickly than food-based MCTs.
- Helps individuals achieve ketosis without extreme carbohydrate restriction.
- Supports mental clarity, focus, and energy for people adapting to low-carb diets.
This is particularly useful in epilepsy management, where ketogenic diets are prescribed to reduce seizures.
Clinical Applications Of MCT Oil
MCT oil has been used in clinical nutrition for decades:
- Fat malabsorption syndromes (e.g., cystic fibrosis, Crohn’s disease, pancreatic insufficiency).
- Short bowel syndrome, where nutrient absorption is limited.
- Enteral nutrition formulas, often enriched with MCTs to improve tolerance.
Neurological conditions, particularly epilepsy and dementia.
Safety, Side Effects, And Precautions
While MCT oil is generally safe, there are important considerations:
Digestive Upset
Common when doses are too high initially nausea, cramps, diarrhea, or bloating.
Liver Function
Since MCTs are processed in the liver, those with advanced liver disease should be cautious.
Diabetes
Type 1 diabetics should monitor ketone levels closely, as excess ketones can trigger ketoacidosis.
Recommended Use
- Start with ½ teaspoon daily.
- Gradually increase to 1–3 tablespoons/day, depending on tolerance.
- The upper safe limit is often cited as 4–7 tablespoons/day.
How To Use MCT Oil
In Coffee (Bulletproof Coffee)
Popularized by keto communities.
In Smoothies Or Shakes
Neutral flavor, easy to mix.
In Salad Dressings Or Sauces
Adds healthy fats without strong taste.
Not Recommended For High-Heat Cooking MCT oil has a low smoke point (~320°F), making it unsuitable for frying.
Consumer Trends And Market Growth
The global MCT oil market has grown rapidly due to increasing demand for ketogenic diets, sports supplements, and functional foods.
Valued at USD 2.3 billion in 2023, projected to grow significantly by 2030 (MarketWatch).
Widely sold as standalone oil, added to nutritional bars, protein powders, and energy drinks.
Key Limitations
Not A Miracle Cure
MCT oil offers benefits, but effects are modest.
Individual Tolerance Varies
Some people experience GI distress even at low doses.
Environmental Impact
Palm-based MCT oil raises sustainability concerns; coconut-derived products are more eco-friendly.
Summary
MCT oil supplements provide a rapid, efficient energy source with benefits ranging from weight management and athletic performance to cognitive support and medical nutrition.
Best for Keto dieters, athletes, people with fat absorption issues, and possibly those with cognitive decline.
Use With caution
Start small to avoid digestive issues; consult a healthcare provider if you have liver disease or diabetes.
Market Reality
While effective, MCT oil should be viewed as a supportive tool, not a cure-all.
MCT Oil VS Whole Foods
Introduction
MCTs (medium-chain triglycerides) can be consumed in two main ways
Supplements form highly concentrated MCT oil or MCT powder.
Whole food sources natural foods rich in MCTs, such as coconut oil, palm kernel oil, dairy products, and certain cheeses.
While MCT oil is prized for purity and rapid absorption, whole foods provide synergistic nutrients like fiber, polyphenols, proteins, and vitamins. Choosing between the two depends on an individual’s health goals, dietary needs, and digestive tolerance.
MCT oil provides maximum efficiency for those wanting ketones or quick energy. However, whole foods offer additional nutrients and culinary flexibility.Coconut Oil VS MCT Oil
Coconut Oil
Contains ~55–65% MCTs, but the majority is lauric acid (C12).
Lauric acid behaves like a hybrid fatty acid partly absorbed like MCTs, partly like long-chain fats.
Provides antimicrobial benefits (due to lauric acid and monolaurin).
Stable for high-heat cooking due to saturated fat content.
MCT Oil
- Refined product, removing longer-chain fats.
- Provides primarily C8 and C10, the fastest-converting fatty acids into ketones.
- Neutral taste and lower smoke point, not ideal for frying.
- Purely functional, not a culinary oil.
Conclusion
Coconut oil is a nutrient-rich food with health-promoting compounds beyond fat, while MCT oil is a performance-oriented supplement for energy and ketosis.
MCT oil and whole food sources of MCTs serve complementary roles
MCT Oil
A supplemental tool for rapid energy, ketosis, and clinical use.
Whole Foods
Provide balanced nutrition, culinary versatility, and synergistic health compounds.
Best Practice
For everyday health, include whole foods rich in MCTs (coconut oil, dairy, goat’s milk). For targeted performance or medical needs, add MCT oil supplementation.
Best MCT Supplement
Introduction
The supplement industry offers a wide variety of MCT products, but not all are created equal. Factors such as MCT composition, purity, sourcing, processing, and sustainability can dramatically affect both the health benefits and environmental impact of these products.
Key Criteria For Choosing The Best MCT Supplement
Composition (C8 vs C10 vs C12)
C8 (Caprylic acid)
The gold standard; converts into ketones most efficiently, least likely to cause GI issues.
C10 (Capric acid)
Effective but slightly slower than C8.
C12 (Lauric acid)
Functions more like a long-chain fat; has antimicrobial properties but weaker ketone production.
Best choice :Supplements that focus on C8 or a C8/C10 blend, depending on purpose.
Safety And Quality Considerations
Even the best MCT supplements can cause side effects if misused
- Start small (½–1 teaspoon/day).
- Avoid cheap products with fillers.
- Verify third-party testing and sustainability claims.
Sustainability And Ethical Choices
Coconut-derived oils are preferable due to sustainability.
Palm-based oils should be RSPO-certified (Roundtable on Sustainable Palm Oil).
Brands like Nutiva emphasize fair-trade and eco-friendly sourcing (Nutiva).
Always check for purity, sourcing, and certifications when choosing a product.
Foods High In MCT
Introduction
While MCT oil provides a concentrated and supplement-based option, many people prefer to obtain MCTs through whole foods. Foods high in medium-chain triglycerides not only deliver these unique fats but also provide proteins, vitamins, minerals, and bioactive compounds that enhance overall nutrition.
The richest sources are coconut oil, palm kernel oil, and dairy products (especially from goats and sheep). Some lesser-known foods like certain cheeses and yogurts also contribute meaningful amounts.
Health Benefits
- Supports heart health in moderation.
- May improve skin and hair health when used topically.
- Provides a natural energy source.
Dairy Products
MCTs naturally occur in smaller amounts in milk, butter, cream, cheese, and yogurt, especially from goats and sheep.
Butter has ~10–15% MCTs (caproic, caprylic, capric acids).
Goat’s milk has a higher MCT proportion than cow’s milk.
Cheeses (like Parmesan, cheddar, goat cheese) contain significant C8, C10.
Nutritional Benefits
Provide protein, calcium, vitamin A, vitamin K2.
Cheese and yogurt may contain probiotics for gut health.
Goat and sheep milk products may be easier to digest.
Specific Foods Rich In MCTs
Here’s a list of some of the best food sources of MCTs
Cream provides a moderate source of MCTs.
Benefits Of Getting MCTs From Whole Foods
- Provides additional nutrients like vitamins, proteins, probiotics.
- Less likely to cause digestive issues than concentrated oil.
- Fits naturally into traditional diets (e.g., Mediterranean goat cheese, tropical coconut).
- More sustainable and balanced when consumed in moderation.
Drawbacks Of Whole Food Sources
Lower concentration of MCTs compared to supplements.
To achieve therapeutic benefits (e.g., ketogenic therapy), whole foods may not provide enough.
Some foods (like palm kernel oil) come with health or sustainability concerns.
Dairy-based MCTs may not be suitable for lactose-intolerant or vegan individuals.
Practical Tips For Including MCT-Rich Foods
Cook With Coconut Oil
Great for stir-fries, baking, or curries.
Add Grass-Fed Butter Or Ghee
Ideal for sautéing and coffee blends.
Incorporate Goat Or Sheep Dairy
Cheese, yogurt, or kefir for gut-friendly MCTs.
Limit Palm Kernel Oil
If consumed, choose RSPO-certified sources.
Combine With Supplements
For ketosis or medical use, pair whole foods with MCT oil for maximum benefit.
Final Words
Foods naturally high in MCTs include coconut oil, palm kernel oil, butter, cream, goat’s milk, and certain cheeses. While they contain fewer MCTs than concentrated oils, they offer synergistic health benefits from proteins, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants.

















